-
Comprehensive control of the multiple dimensions of a light beam, such as phase, amplitude, polarisation, and orbital angular momentum (OAM), represents one of the most compelling frontiers in modern photonics. Mastering the full suite of dimensions is key to unlocking transformative advances in high-capacity communications, secure encryption, and optical computing systems. In this context, the emergence of metasurfaces, which are engineered two-dimensional materials composed of subwavelength nanostructures, provides a paradigm-shifting solution. By offering local control over the wavefront of light, these ultrathin platforms can modulate various parameters of light, such as phase, amplitude, and polarisation, enabling imaging1–5, holography6–10, and structured beams11–13. However, the integration of these independent controls into a unified, single-element device capable of projecting complex, information-rich, and spatially variant light fields into a three-dimensional volume remains a critical challenge. Previous results have largely been limited to two-dimensional systems or have involved significant trade-offs among different parameters. Consequently, the broader possibilities of volumetric optical landscapes with multiple parameters remain largely unknown.
In a recently published paper on Light: Science & Applications, Zhang et al. conceived and realised a novel metasurface platform that generates a full-parameter-modulated three-dimensional vectorial generalised vortex beam (GVB) array14. This work represents a paradigm shift towards holistic light-field synthesis, pushing the frontiers of multidimensional optical control. The recent concept of GVBs has added a new layer of flexibility by allowing custom-designed non-linear azimuthal phase gradients. This breaks the rigid doughnut intensity profile of traditional vortex beams, enabling intuitive graphical representations of mathematical operations and other novel functionalities15,16. The current work elevates this concept by creating not only a single GVB but also an entire 3D array, each with independently tailored properties.
This study aims to promote Dammann vortex optimisation, as shown in Fig. 1. The principle of Dammann gratings, which efficiently split a beam into an array of uniform-intensity spots, was combined with the phase manipulation ability of vortex metasurfaces and a zone plate for longitudinal control. Through an analytical model and joint optimisation, a metasurface was designed that projects a 3D lattice of diffraction orders. Each order (m,n,q) in this lattice acts as an independent channel carrying a unique GVB with a predefined intensity profile and polarisation state. Researchers developed two distinct implementations to showcase their concepts. In the first study, a geometric phase metasurface with rotating silicon nanofins was used to create a scalar 3D GVB array. In this array, the intensity profile of each beam, forming a five-pointed star or classic doughnut, can be spatially varied and controlled based on the sum of its diffraction indices m + n + q. A more advanced implementation employs a birefringent metasurface composed of rectangular nanopillars. This design allows for independent phase modulation of two orthogonal linear polarisation channels. Through a "vectorial Dammann optimisation" process, the team endowed each of the 27 diffraction orders in a 3 × 3 × 3 array not only with a distinct intensity profile but also with an arbitrary polarisation, including horizontal, vertical, diagonal, anti-diagonal, left and right handedness circular polarisations.
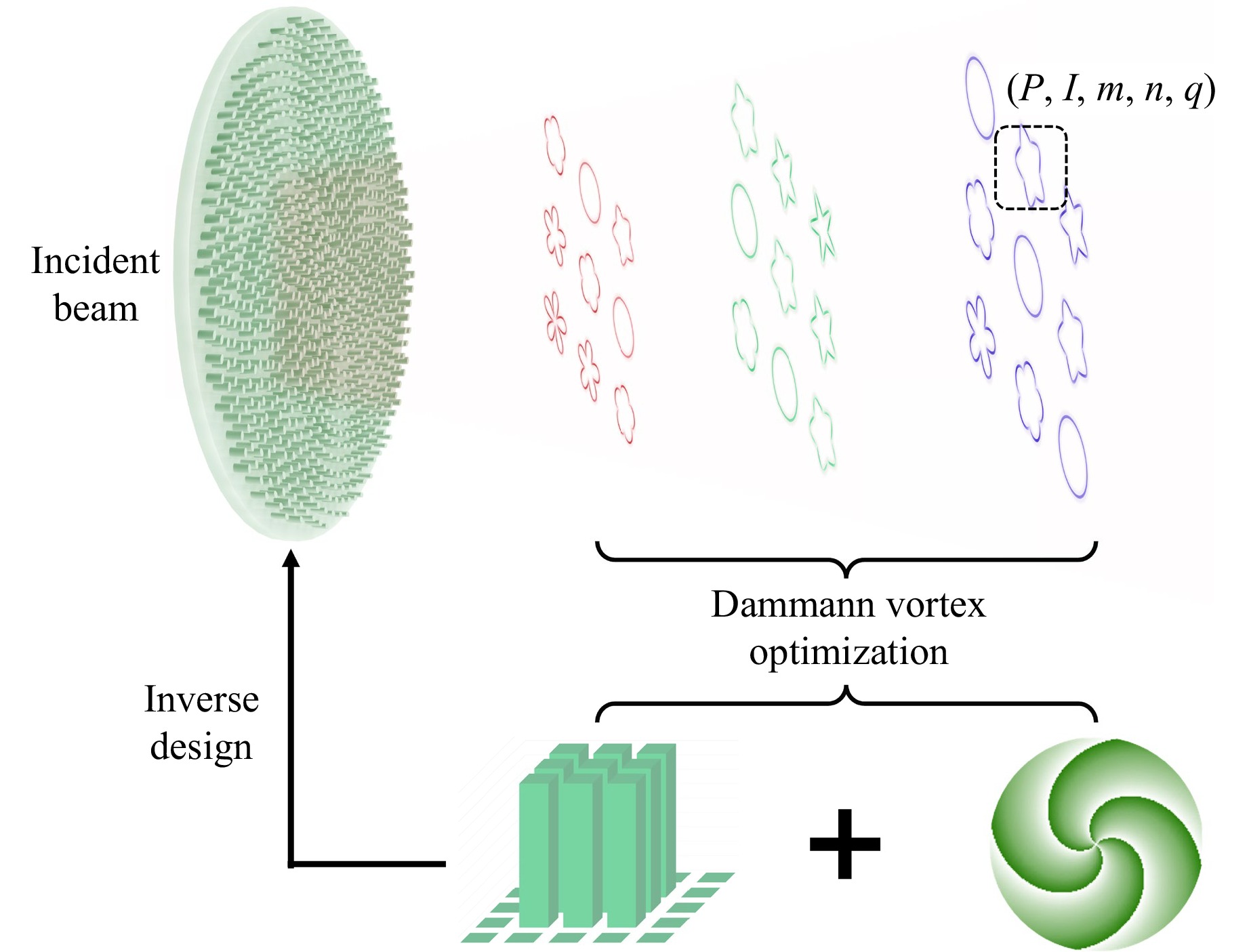
Fig. 1 Illustration of metasurfaces for full-parameter optical wavefront engineering. The 3D GVB arrays (m,n,q) are characterised by spatial intensity features (I) and polarisations (P), which are generated through the development of Dammann vortex optimisation.
In summary, this technology demonstrates the potential of metasurfaces to replace complex multicomponent optical systems with single compact devices. The integration of full-parameter control into compact metasurface platforms represents a significant advancement towards the practical implementation of complex optical systems. As fabrication techniques continue to improve, we anticipate that these devices will be implemented in practical systems for communication, sensing, and computing applications.
Metasurfaces for full-parameter optical wavefront engineering
- Light: Advanced Manufacturing , Article number: (2026)
- Received: 04 December 2025
- Revised: 13 December 2025
- Accepted: 15 December 2025 Published online: 15 January 2026
doi: https://doi.org/10.37188/lam.2026.010
Abstract: Multidimensional light-field control is opening new frontiers in photonics. Recent breakthroughs in metasurface design and the integration of Dammann optimisation with spin-decoupled phase modulation enable the simultaneous manipulation of phase, amplitude, polarisation, and orbital angular momentum to project information into three-dimensional space. This paradigm shift towards full-parameter control in stereoscopic volumes is promising for revolutionising applications from high-capacity optical communications to secure encryption and parallel computing, marking a significant advancement in integrated photonic systems.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article′s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article′s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: