View by Category
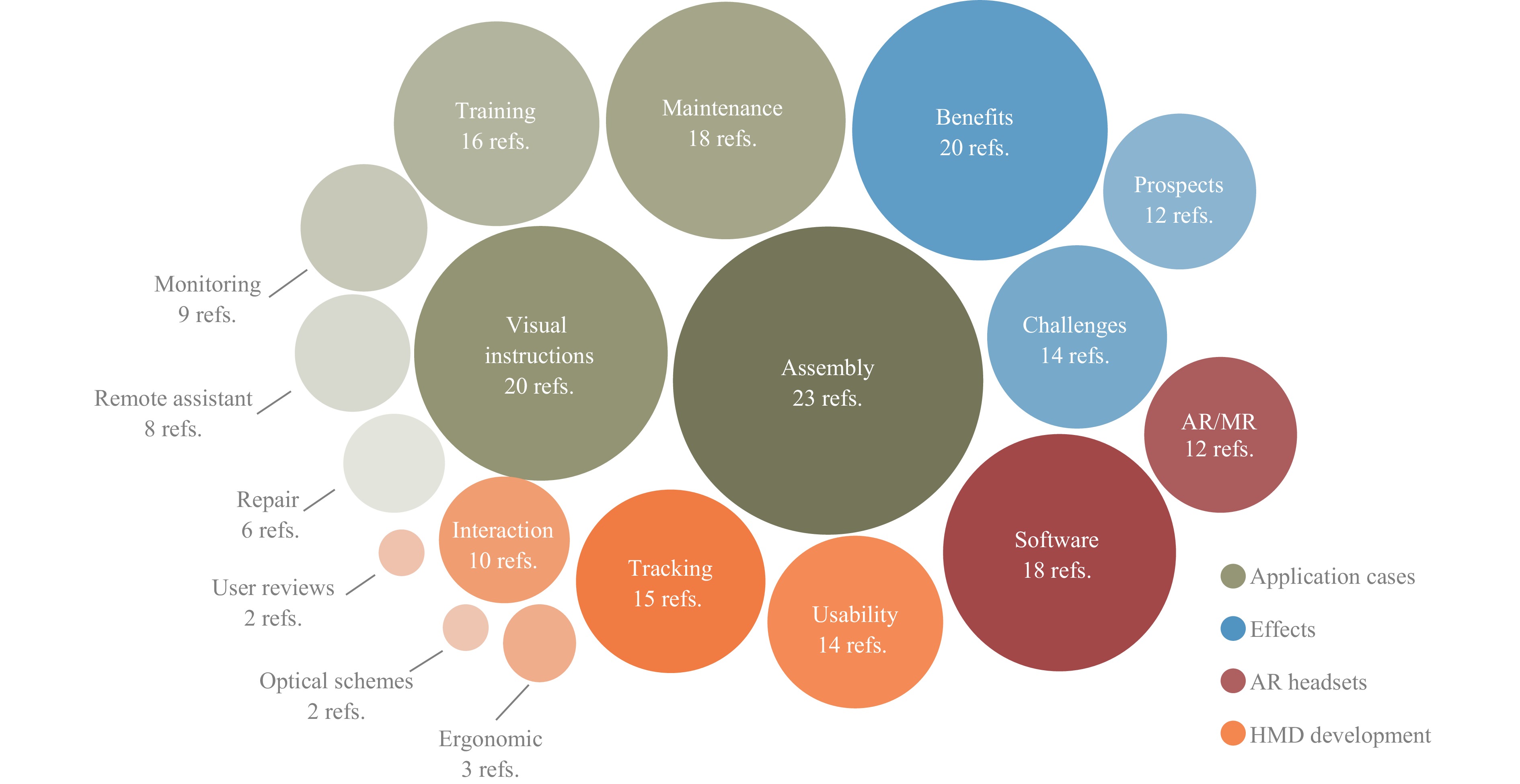
This review considers the modern industrial applications of augmented reality headsets. It draws upon a synthesis of information from open sources and press releases of companies, as well as the first-hand experiences of industry representatives. Furthermore, the research incorporates insights from both profile events and in-depth discussions with skilled professionals. A specific focus is placed on the ergonomic characteristics of headsets: image quality, user-friendliness, etc. To provide an objective evaluation of the various headsets, a metric has been proposed which is dependent on the specific application case. This enables a comprehensive comparison of the various devices in terms of their quantitative characteristics, which is of particular importance for the formation of a rapidly developing industry.
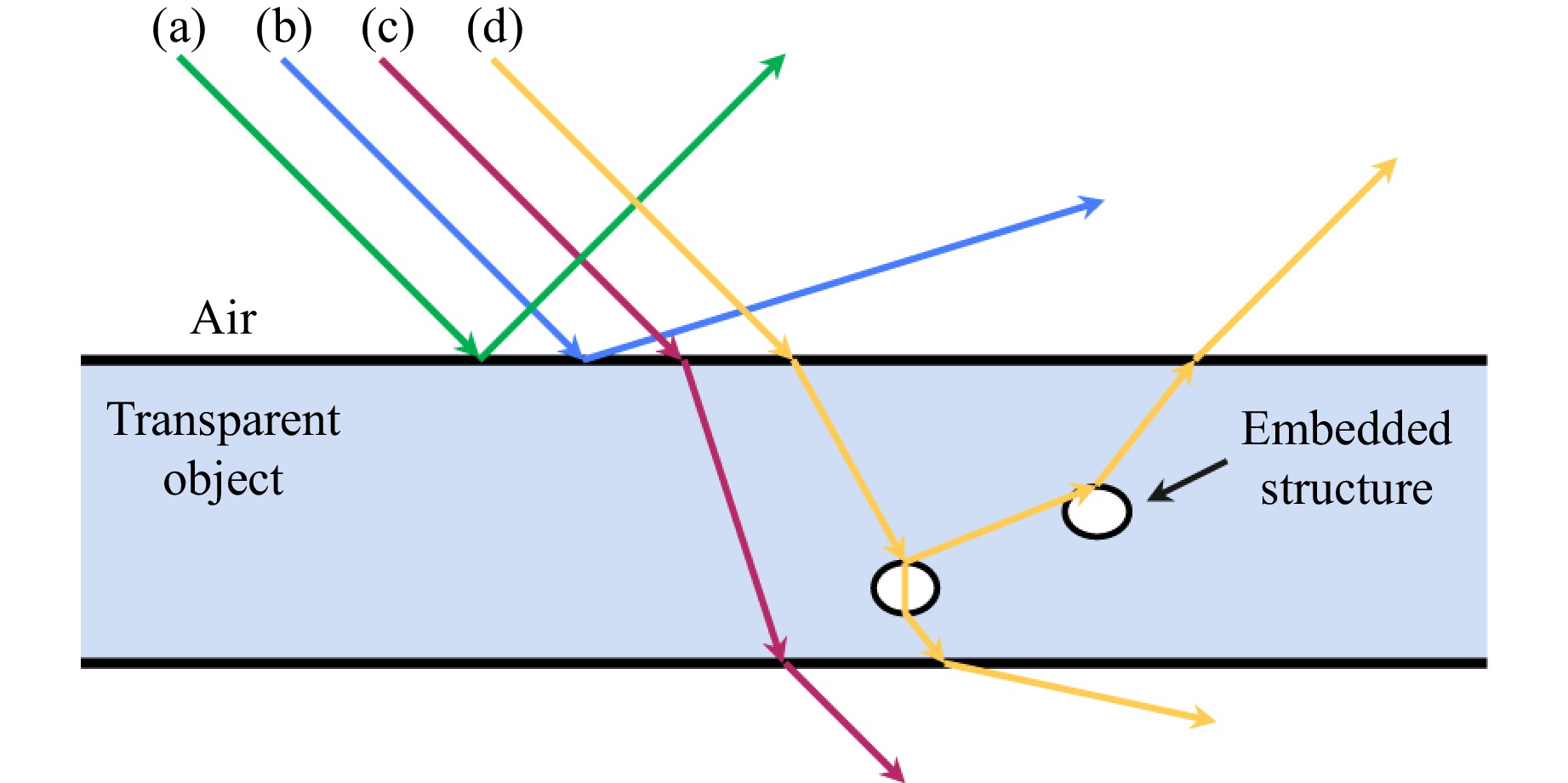
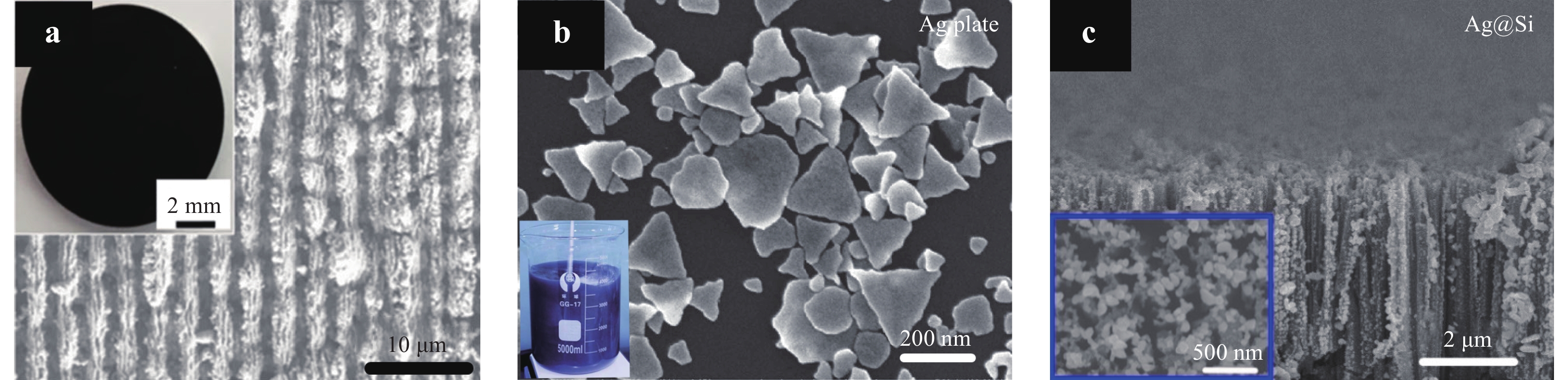
Transparent objects are widely used in various fields, leading to increasing demand for methods of measuring them. However, the measurement of such objects has always been challenging owing to the intricate refraction and reflection phenomena they exhibit. Given that traditional contact measurement methods can damage transparent objects, the use of non-destructive measurement techniques, particularly those based on optical principles, is considered preferable. As a result, various non-destructive measurement methods have been developed for transparent objects by leveraging the unique characteristics of light, and a comprehensive review is imperative for exploring these innovative methods and their potential applications. This review accordingly begins by elucidating the necessity of measuring transparent objects and exploring the concept of transparency. Next, an overview of various non-destructive optical measurement techniques spanning macro-, micro-, and general-scale applications is presented, followed by a discussion of their respective advantages and limitations. Finally, the paper concludes by outlining future directions for potential advancements in the field. This review is expected to serve as a valuable resource for newcomers in the field of transparent object measurement and assist researchers seeking to integrate these techniques into interdisciplinary studies.




 Email
Email RSS
RSS