View by Category
Published
, Published online: 12 January 2026
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2026.002
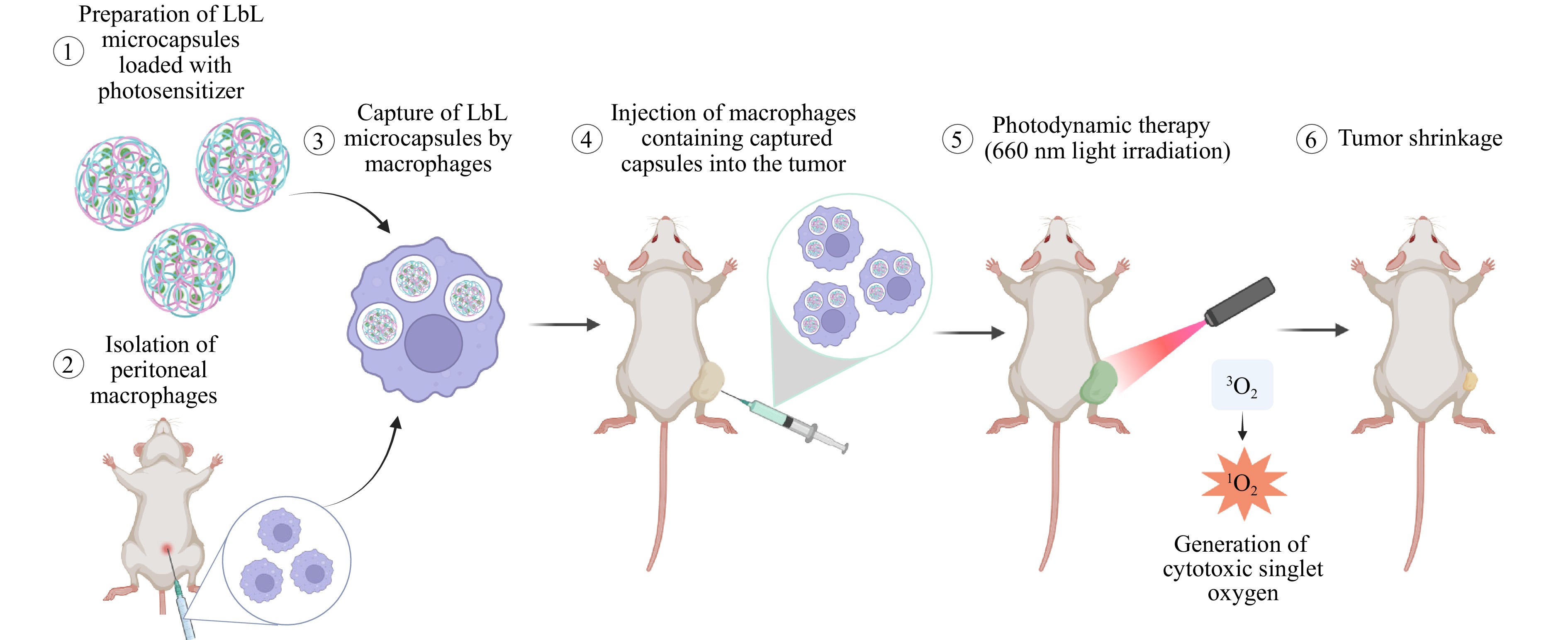
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a promising strategy for treating solid tumours due to its spatially controlled, light-triggered cytotoxicity. Although recent advances in optical technologies have improved light delivery, PDT efficacy remains limited by insufficient drug accumulation in tumours, largely due to the complexity of the tumour microenvironment. To address this challenge, a macrophage-mediated delivery platform was developed using layer-by-layer (LbL) microcapsules loaded with second-generation photosensitizers: photoditazine (PD) and aluminum tetrasulfophthalocyanine chloride (PS). Both photosensitizers exhibited low dark toxicity and high phototoxicity, enabling their safe transport by carrier cells. The photosensitizers were efficiently encapsulated into LbL microcapsules (6.2 ± 0.5 μm) with different shell compositions. Significant differences were observed between macrophage types: RAW 264.7 macrophages predominantly retained capsules on the cell surface, whereas primary peritoneal macrophages (PMs) internalised capsules within 3 h and retained them for up to 6 d without degradation. Among the tested formulations, polyarginine/dextran sulfate ((PArg/DS)4) capsules loaded with PD demonstrated the highest uptake efficiency and supported macrophage migration into tumour spheroids. In vivo experiments using a CT-26 colon cancer model confirmed the therapeutic potential of this platform, while highlighting the need for further optimisation for large tumours. This study provides new insights into cell-mediated delivery systems and underscores their potential to enhance PDT outcomes beyond current limitations.
Published
, Published online: 31 March 2021
, doi: 10.37188/lam.2021.006
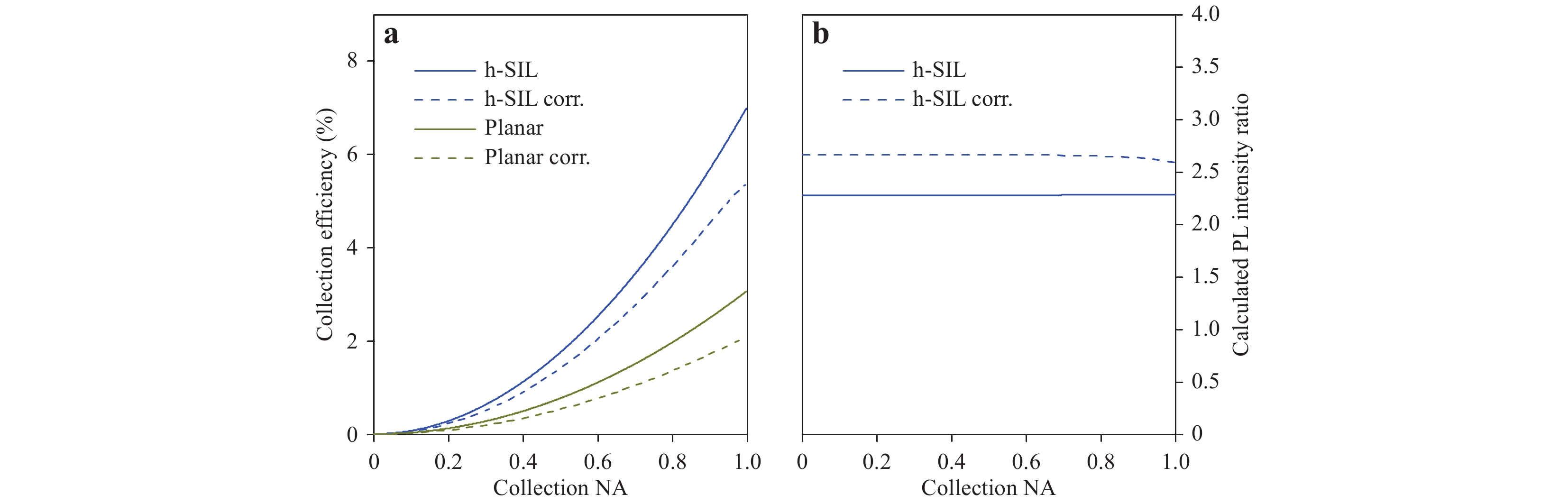
Future quantum technology relies crucially on building quantum networks with high fidelity. To achieve this challenging goal, it is of utmost importance to connect individual quantum systems such that their emitted single photons overlap with the highest possible degree of coherence. This requires perfect mode overlap of the emitted light from different emitters, which necessitates the use of single-mode fibres. Here, we present an advanced manufacturing approach to accomplish this task. We combined 3D printed complex micro-optics, such as hemispherical and Weierstrass solid immersion lenses, as well as total internal reflection solid immersion lenses, on top of individual indium arsenide quantum dots with 3D printed optics on single-mode fibres and compared their key features. We observed a systematic increase in the collection efficiency under variations of the lens geometry from roughly 2 for hemispheric solid immersion lenses up to a maximum of greater than 9 for the total internal reflection geometry. Furthermore, the temperature-induced stress was estimated for these particular lens dimensions and results to be approximately 5 meV. Interestingly, the use of solid immersion lenses further increased the localisation accuracy of the emitters to less than 1 nm when acquiring micro-photoluminescence maps. Furthermore, we show that the single-photon character of the source is preserved after device fabrication, reaching a \begin{document}$ g^{(2)} (0)$\end{document} ![]()
![]()




 Email
Email RSS
RSS